PRONOUNS
PRONOUNS
In grammar, a pronoun is defined as a word or phrase that may be substituted for a noun or noun phrase, which once replaced, is known as the pronoun’s antecedent. How is this possible? In a nutshell, it’s because pronouns can do everything that nouns can do. A pronoun can act as a subject, direct object, indirect object, object of the preposition, and more.
Without pronouns, we’d have to keep on repeating nouns, and that would make our speech and writing repetitive, not to mention cumbersome. Most pronouns are very short words. Examples include:
- He
- She
- They
- It
- We
- Who
As mentioned, pronouns are usually used to replace nouns, however they can also stand in for certain adverbs, adjectives, and other pronouns. Anytime you want to talk about a person, animal, place or thing, you can use pronouns to make your speech or writing flow better.
Types of Pronouns
- Indefinite pronouns : those referring to one or more unspecified objects, beings, or places
- personal pronouns : those associated with a certain person, thing, or group; all except you have distinct forms that indicate singular or plural number
- Reflexive pronouns those preceded by the adverb, adjective, pronoun, or noun to which they refer, and ending in –self or –selves
- Demonstrative pronouns those used to point to something specific within a sentence
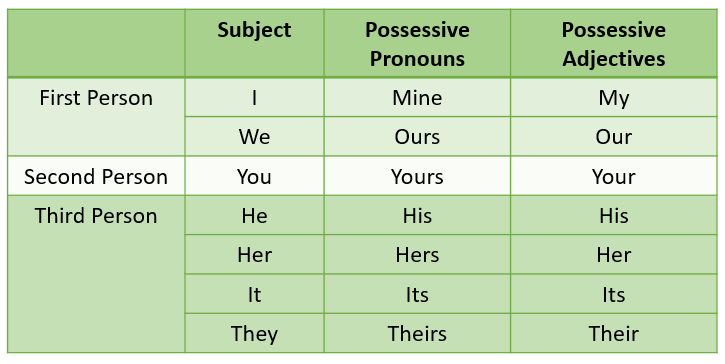
- Possessive pronouns those designating possession or ownership
- Relative pronouns : those which refer to nouns mentioned previously, acting to introduce an adjective (relative) clause
- Interrogative pronouns : those which introduce a question
- Recicprocal pronouns : those expressing mutual actions or relationship; i.e. one another
- Intensive Pronouns : those ending in –self or –selves and that serve to emphasize their antecedents
Examples
- Don’t tell me that you can’t go with us.
- Anybody who says it won’t be fun has no clue what they are talking about.
- These are terribly steep stairs.
- We ran into each other at the mall.
- We ran into each other at the mall.


Choose the appropriate options to complete the sentences.
1. We all told the boss that we wanted to have ---- salaries paid in advance but he just ignored ----.
A) ours / it
B) his / we
C) their / our
D) we / his
E) our / us
2. When the man asked me how I had got ---- address, I told him that I was given it by a relative of ----.
A) my / me
B) his / his
C) mine / his
D) his / him
E) him / him
3. Although ---- in the room seemed to follow ---- said by the speaker, he never intended to simplify his language.
A) no one / anything
B) anybody / anything
C) nobody / nothing
D) anyone / nothing
E) someone / something
A) my / me
B) his / his
C) mine / his
D) his / him
E) him / him
3. Although ---- in the room seemed to follow ---- said by the speaker, he never intended to simplify his language.
A) no one / anything
B) anybody / anything
C) nobody / nothing
D) anyone / nothing
E) someone / something
4. I hope you will enjoy ---- at the re-union party this weekend because I won't be able to be there ----.
A) you / myself
B) yourself / mine
C) yours / oneself
D) yourself / myself
E) you / me
5. We decided to do all the cooking ---- instead of hiring a catering company for the party.
A) of our own
B) oneself
C) by ourselves
D) ours
E) each other
A) of our own
B) oneself
C) by ourselves
D) ours
E) each other



Comentarios
Publicar un comentario