PREPOSITIONS AND CONJUNCTIONS
PREPOSITIONS AND CONJUNCTIONS
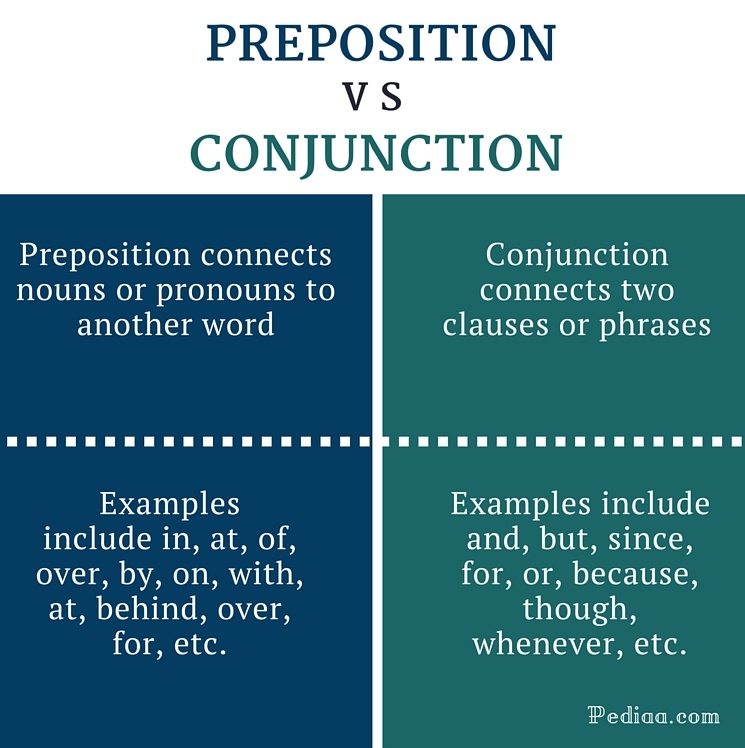
A preposition is a word used to express some relation of different things or thoughts to each other, and is generally placed before a noun or a pronoun: as,
- "The paper lies before me on the desk."
In that sentence, before is the preposition, me is the governed term of a preposition, "before me" is a prepositional phrase, and the verb lies is the prior term of a preposition. "On the desk" is the other prepositional phrase, and lies is its prior term.
To a preposition, the prior term may be a noun, an adjective, a pronoun, a verb, a participle, or an adverb; and the governed term may be a noun, a pronoun, a pronominal adjective, an infinitive verb, or a participle.
Although overlooked in common speech, prepositional phrases should not be placed at the end of a question: as,
- "Who do I give this to?"
- Say, "To whom do I give this?"
Prepositional phrases can be placed at the end of a sentence: as,
- "She did not sign up for tennis
See also: List of English prepositions
Some words are linked with their prepositions, e.g. compared with, similar to, and different from (possibly different than in USA).
Commonly used prepositions include:
Prepositions
- About—In concern with; engaged in; intent on; on the point or verge of; in act of; concerning; with regard to; on account of.
- Above—In or to a higher place; on or over; superior to; surpassing; beyond; higher in measure or degree.
- Across—From side to side; athwart; crosswise; quite over.
- After—Behind in place; below in rank; later in time; subsequent to; following; in search of; in pursuit of; concerning; in relation to; in imitation of; in conformity with; after the manner of; according to; in accordance with; in proportion to.
- Against—Abreast; opposite to; facing; towards; in opposition to; counter to; in contrariety to; adverse to; by of before the time; in preparation for
Conjunctions
A conjunction is a word used to connect words or sentences in construction, and to show the dependence of the terms so connected: as,
- "You and he are happy, because you are good."—Murray.
Conjunctions are divided into two general classes, copulative and disjunctive; and a few of each class are particularly distinguished from the rest, as being corresponsive.
A copulative conjunction is a conjunction that denotes an addition, a cause, a consequence, or a supposition: as,
- "He and I shall not dispute; for, if he has any choice, I shall readily grant it."
The copulatives: and, as, both, because, even, for, if, that, then, since, seeing, so.
A disjunctive conjunction is a conjunction that denotes opposition of meaning: as,
- "Though he were dead, yet shall he live."—St. John's Gospel.
- "Be not faithless, but believing."—Id.
The disjunctives: or, nor, either, neither, than, though, although, yet, but, except, whether, lest, unless, save, provided, notwithstanding, whereas.

PREPOSITIONS AND CONJUNCTIONS




Comentarios
Publicar un comentario